On Theory: Why Graph Theory is Essential Knowledge for All Industries Today
Introduction
"Entities should not be multiplied without necessity" -- Ockham's Razor Principle
Graph Theory is a mathematical foundational theory that has been severely underestimated by the public. It doesn't study images, pictures, or charts, but rather an abstract and simple mathematical theory. The graph in graph theory is an abstract concept, very similar to a relationship network, with corresponding nodes (or vertices), and associative relationships or edges between nodes. Graph theory concepts are very simple: graphs, nodes, and edges. This article will briefly introduce basic concepts of graph theory and its applications in the real world. (Note! This is not a scientific paper, so there won't be boring mathematical formulas - please enjoy reading)
Graph Theory Overview
In graph theory, there are three important concepts:
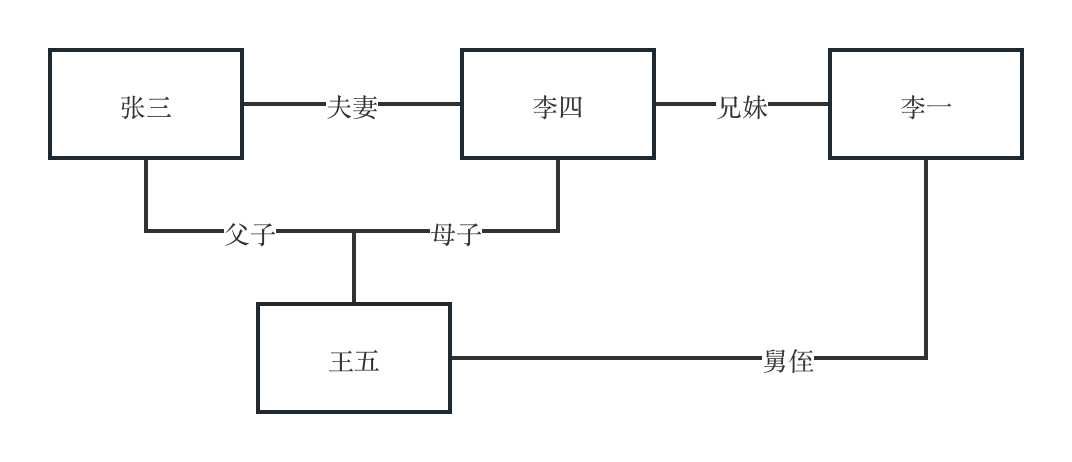
- Node: Can be understood as an entity, such as Zhang San, Li Si, Wang Wu in a relationship network;
- Edge: Can be understood as relationships between entities, for example, Zhang San and Li Si are husband and wife, Wang Wu is their son;
- Graph: Can be understood as the collection of all nodes and edges, such as the happy family composed of Zhang San, Li Si, and Wang Wu.
From these three basic concepts, we can infer relationships between nodes. For example, Li Si's older brother Li Yi would be Wang Wu's uncle, and Wang Wu would be his nephew.
Of course, graph theory applications go far beyond this. In our real world, graph theory applications are so widespread that ordinary people can hardly perceive their existence.
Below, we'll introduce common applications of graph theory in the technology field.
Search Engines
Google, Baidu, Bing - these are all search engines we use daily. When we need to learn about something, we usually open a search engine, enter keywords, and the search engine returns relevant results that are usually extremely accurate. Actually, the core theory behind search engine technology is graph theory.
We can imagine each web page of a website as a node, hyperlinks on pages as corresponding edges, and the website as a graph containing all web pages (nodes) and webpage relationships (edges), as shown below.
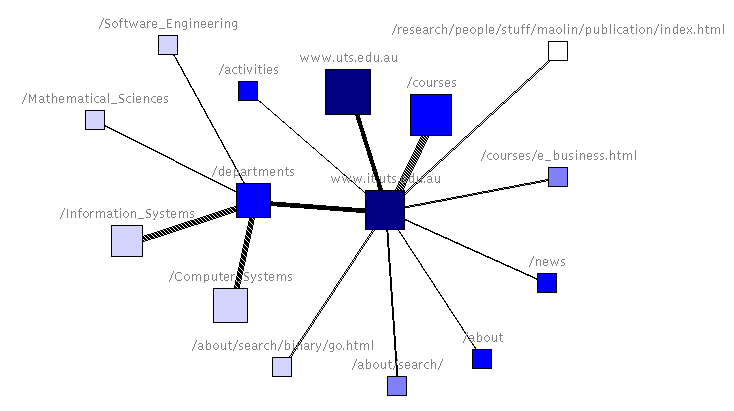
The reason search engines can magically return search results to users is through clever application of the PageRank algorithm, which represents node relationships using linear algebra, then calculates nodes or web pages most similar to keywords, finally achieving basic search functionality. Friends interested in PageRank algorithm can check relevant materials - there are many online, so I won't elaborate.
Natural Language
Natural Language is actually languages used by natural humans in conversation, such as Chinese, English, Japanese, etc. For example, Zhang San telling Li Si "I love you," or you asking a friend "I discovered an amazing coffee shop downtown last week, want to go together this weekend?", or even all the text in this article - all are natural language.
So what's the relationship between graph theory and natural language? Actually, if we think carefully, we'll find that Chinese has three parts of speech: subject, predicate, and object, such as the simple subject-predicate-object sentence "I love you." In reality, this sentence can be represented by a graph, where the subject ("I") and object ("you") are nodes, and the predicate ("love") is an edge, representing the relationship from subject to object. Of course, for complex sentences, relationships become more complex, and corresponding graphs become more complex, but they can always be represented using graphs, nodes, and edges to show relationships between words.
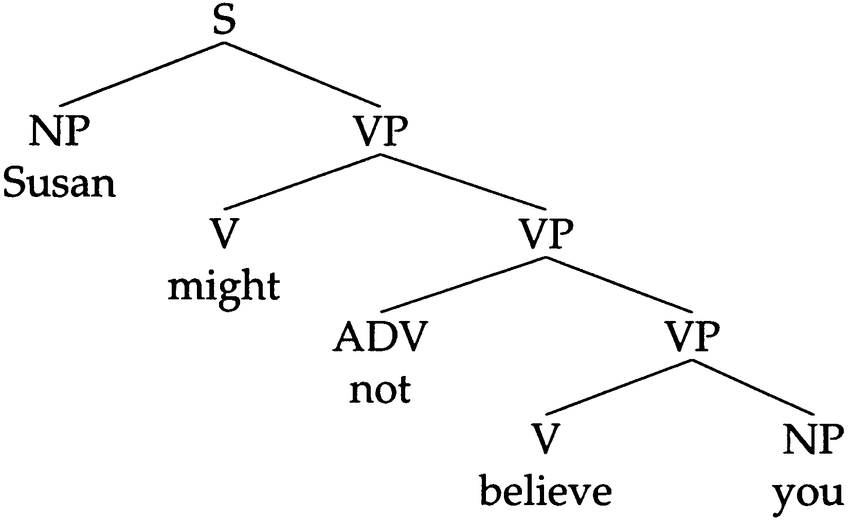
The diagram below represents the sentence "Susan might not believe you" as a graph, which is a tree structure. A tree is also a type of graph - a special structure.
Currently popular translation software, speech recognition, chatbots, etc., all have Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology behind them that comes from graph theory.
Food for thought: Can program code (like Python) be processed using graph theory?
Artificial Intelligence
Recently, Artificial Intelligence technology has become very popular, with core technology coming from deep neural networks, a special form of neural networks. Neural network concepts can be simply understood as structures similar to brain neural networks composed of neurons. Electrical signals from some neurons in the brain are transmitted to other neurons through neural networks, producing abstract concepts like consciousness, thoughts, and cognition. The logic behind this is very simple - electrical signal triggering, just in extremely large quantities. The success of today's deep neural networks also benefits from large-scale neural network computing systems built on computers. The GPT-3 language model from globally famous AI company OpenAI consists of 175 billion parameters, approaching the order of magnitude of adult brain neurons.
Everything is Graph Theory
Graph theory concepts are very simple, like abstract concepts of atoms, molecules, and chemical bonds in the physical world, making them easy to process mathematically. Therefore, from the global internet to protein molecular structures, graph theory can be widely applied in most fields of the real world. Thus, learning graph theory well is very helpful for solving real problems in our work, life, and study. For example, optimal time scheduling problems can be modeled using graph theory; pivot tables commonly used by white-collar workers can also be processed using bipartite graphs from graph theory. Recently, I've also been trying to apply graph theory to intelligent web information extraction technology. Learning graph theory helps us better understand this world, allowing us to more reasonably handle our own lives and work.
Community
If you're interested in my articles, you can add my WeChat tikazyq1 with note "码之道" (Way of Code), and I'll invite you to the "码之道" discussion group.
